Vol. 1, Issue 4 (2013)
Polymer Supported Sodium Chromate Oxidation of 1-Phenylethanol: A Kinetic Mechanistic Study
Author(s): Vilas Y. Sonawane
Abstract: Oxidation of organic compounds is quite important from synthetic and technological view points. Many of the industrially important organic compounds like aldehydes, ketones, acids, etc. can be produced by the oxidation of related substrate by the use of suitable oxidizing agents. The kinetics of the oxidation of 1-Phenylethanol (PE) by PS-Chromate has been followed by monitoring the increase in the absorbance of reaction intermediate. The reaction followed by zero order behavior, being zero order in each reactant. The rate of reaction increase with increase in weight of oxidant, concentration, temperature and dielectric constant of the solvent. A free radical scavenger affects the reaction rate. The stiochiometry has been found to be 1mol PE: 1mol of Chromate. Thermodynamic parameters evaluated are [Ea] = 75 KJ mol-1, [∆H#]=56 KJ mol-1, [∆S#]=-69 JK mol-1, [∆G#] =298KJ mol-1, and [A] =3.4 x 10-5s-1 results under pseudo zero order conditions are in agreement with the rate law. In agreement with the rate law, the 1/k2 versus [H+] profile passes through the minimum. Main reaction product acetophenone isolated and characterized.
Related Graphics: Click here for more related graphics
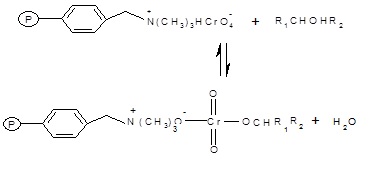
Fig. 1: The polymer supported reagent reacts with a molecule of 1-Phenylethanol to form a chromate ester.
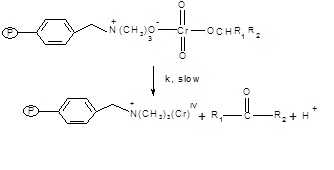
Fig. 2: The ester formed will decompose into ketone and the intermediate chromium (IV) will be formed in the second and slow step.
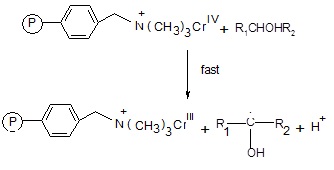
Fig. 3: The intermediate chromium (IV) thus reacts with another alcohol molecule to produce a free radical species.
Pages: 40-44 | 2098 Views 136 Downloads
download (5563KB)
How to cite this article:
Vilas Y. Sonawane. Polymer Supported Sodium Chromate Oxidation of 1-Phenylethanol: A Kinetic Mechanistic Study. Int J Chem Stud 2013;1(4):40-44.






