Vol. 1, Issue 4 (2013)
Polymer Supported Sodium Chromate Oxidation of 1-Phenylethanol: A Kinetic Mechanistic Study
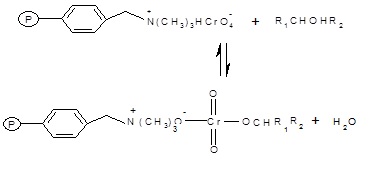
Fig. 1: The polymer supported reagent reacts with a molecule of 1-Phenylethanol to form a chromate ester.
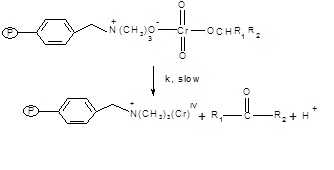
Fig. 2: The ester formed will decompose into ketone and the intermediate chromium (IV) will be formed in the second and slow step.
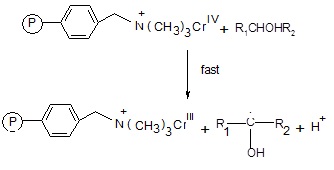
Fig. 3: The intermediate chromium (IV) thus reacts with another alcohol molecule to produce a free radical species.
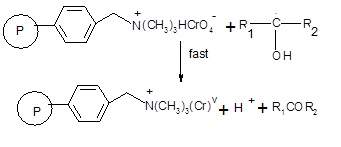
Fig. 4: Subsequently the free radical will react with another oxidant site in the polymeric reagent in a fast step leading to the formation of chromium (V).
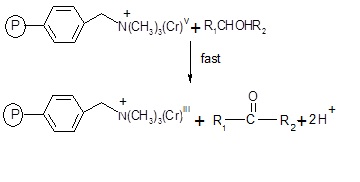
Fig. 5: The intermediate chromium (V) in the last step reacts with 1-phenylethanol produce acetophenone.




