Vol. 7, Issue 2 (2019)
Characterization of plant growth promotion and disease control trends of rhizobacteria isolated from Umorok (Capsicum chinense)
Author(s): Phazna Devi TA, Dinabandhu Sahoo, Aravind Setti, MC Kalita and Sarangthem Indira Devi
Abstract: The aim of the study is to identify and characterize the rhizosphere bacteria of King Chili locally known as Umorok plant (Capsicum chinense) and evaluates their plant growth promotion and defense from pathogens. A total of 300 rhizobacteria were isolated from three different growth stages of king chili viz.; juvenile, flowering and fruiting growth stages and characterized to establish the beneficial role. Nevertheless, the isolated microorganisms were evaluated for their in-vitro plant growth promotion potential by performing biochemical tests and pathogen antagonistic activities by dual culture methods. Out of the total isolates, 10 potential rhizobacteria were selected for pot culture experiment based on their multiple Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) and biocontrol activity. Since these inoculants exhibited multiple trait benefits to the host plant, they can be adapted as potential bio-inoculant consortia for plant health improvement and disease control to increase Umorok productivity.
Related Graphics: Click here for more related graphics
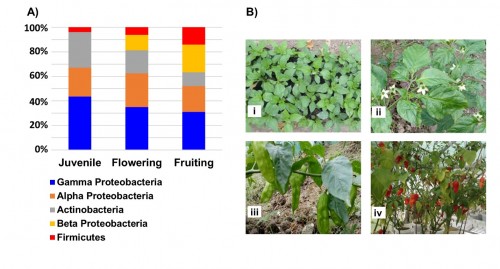
Fig. 1: Three different growth stages of umorok rhizosphere are being associated with different types of bacterial species; however, all the identified rhizobacteria were representatives of six classical phyla. A) More bacterial diversity was observed in flowering and fruiting stages with additional beta proteobacteria that were not showing up in the juvenile stage. In the comparative analysis, gamma proteobacteria emerged as the most abundant bacterial variety and Firmicutes were turned out to be least showed organisms in all the three stages of the plant life cycle. B) The juvenile (i), flowering (ii), fruiting (iii), and matured (iv) stages of the umorok plant
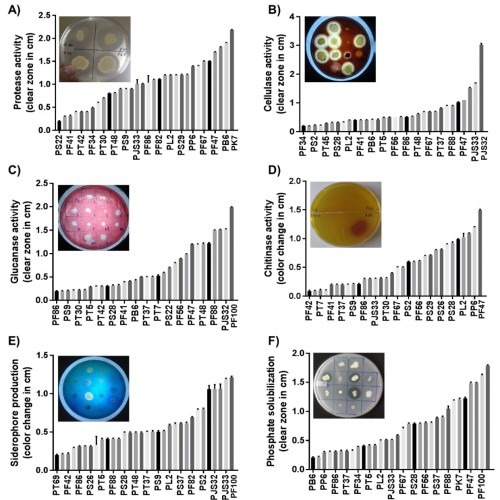
Fig. 2: Biochemical test results of 32 potential umorok rhizobacteria along with characteristic biochemical activity clear zone, colony morphology, and color of media in agar plates: A) protease activity B) cellulase activity C) glucanase activity D) chitinase activity E) siderophore production and F) Phosphate solubilization
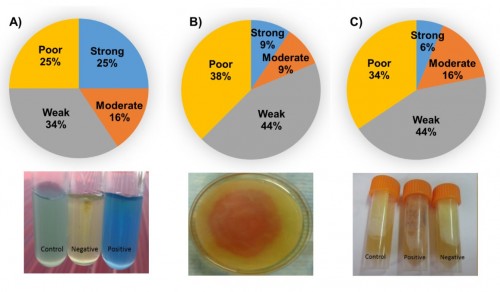
Fig. 3: Qualitative biochemical tests performed on umorok rhizosphere to demonstrate the action potential based on characteristic color change: A) Nitrogen fixing assay revealed 25% of the assayed bacteria exhibited strong activity, and the color score was attributed based on the blue color intensity observed at the end of the assay, B) IAA production assay showed 9% of the bacteria exhibited strong IAA production, and the activity was measured based on the characteristic red color zone around the rhizobacterial colony, and C) HCN production assay witnessed 6% of the strong bacteria among tested microorganisms based on the color change from yellow to brown or reddish brown
Pages: 313-321 | 626 Views 121 Downloads
download (14845KB)
How to cite this article:
Phazna Devi TA, Dinabandhu Sahoo, Aravind Setti, MC Kalita, Sarangthem Indira Devi. Characterization of plant growth promotion and disease control trends of rhizobacteria isolated from Umorok (Capsicum chinense). Int J Chem Stud 2019;7(2):313-321.






