Vol. 7, Issue 2 (2019)
Sensitivity of modified DMAB test for lower level detection of urea in milk
Author(s): Zala Siddharajsinh, Tanmay Hazra, Parmar Manishkumar Pratapsinh, Govani Radhika, Akshay Ramani and VM Ramani
Abstract:
Milk is perhaps the most widely adulterated food commodity. There are different adulterants that used in milk like urea, skim milk, washing powder, water, salt, sugar, oil etc. Urea adulteration in milk is very common and frequent in India, as it is the main components of non-protein nitrogen in milk, so external addition of urea increase total nitrogen in milk, so SNF contain use to be increased. As India is an agriculture based country where urea is often used as fertilizer or as a base material for cattle feed formulation. So urea is commonly available in every house hold of dairy farmers.
Wet chemistry based method (DMAB test), suggested by FSSAI is mostly usable methodology for detection of urea in milk. However the maximum detection limit for this method is 0.2%, also for preparation of DMAB reagent ethyl alcohol been recommended, that is some time difficult to procure for sate like Gujarat. So this method should be modify in a view to increase better sensitivity as well as easy availability. In our present research DMAB solution was prepared using isopropanol. Using this standardized said protocol urea could be detected 0.05% (cow), and 0.1% (buffalo) milk respectively.
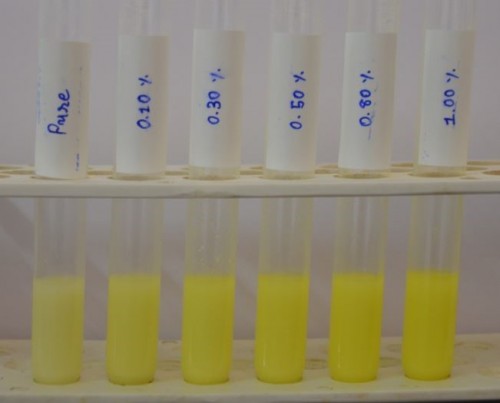
Fig. 1: LoD of modified DMAB test performed in buffalo milk
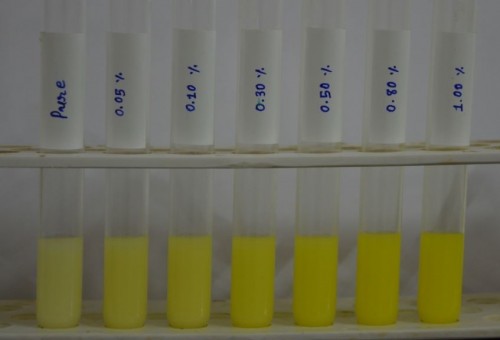
Fig. 2: LoD of modified DMAB test performed in cow milk
Pages: 10-12 | 1395 Views 170 Downloads
download (5499KB)
How to cite this article:
Zala Siddharajsinh, Tanmay Hazra, Parmar Manishkumar Pratapsinh, Govani Radhika, Akshay Ramani, VM Ramani. Sensitivity of modified DMAB test for lower level detection of urea in milk. Int J Chem Stud 2019;7(2):10-12.






