Vol. 7, Issue 1 (2019)
Effect of Zinc application on soil properties and uptake of nutrients by wheat grown on calcareous soil
Author(s): Mohini Patle, AG Durgude, MR Chauhan and AD Kadlag
Abstract: The present field experiment was conducted at PGI, Research Farm. Department of Soil Science and Agril. Chemistry, M.P.K.V., Rahuri, during the Rabi 2016-17. The experiment was laid out in a randomized block design with three replication and nine treatments. The treatment comprised of T1: Absolute control, T2: General recommended dose of fertilizer 120:60:40 kg ha-1 N: P2O5:K2O + 10 t FYM ha-1, T3: GRDF with soil application of ZnSO4 @ 20kgha-1, T4: GRDF with 120 kg N through zinc coated urea + 60:40 P2O5:K2O kg ha-1 + 10 t ha-1 FYM, T5: GRDF with soil application of cow dung slurry with ZnSO4, T6: GRDF with soil application of 100 kg FYM + ZnSO4 @20kgha-1, T7: GRDF with seed coating treatment of ZnSO4 @ 20kgha-1, T8: GRDF with seed coating treatment of chelated Zn EDTA and T9: GRDF with seed treatment of zinc solubilizing bacteria + soil application of zinc sulphate @ 20kgha-1. The results of investigation revealed that the application of different methods of zinc in soil was influenced the soil properties. The available nutrients N,P and K at harvest were found to be significantly increased due to treatment of GRDF +soil application of ZnSO4 @ 20kgha-1 with 100 kg FYM incubated for one week and treatment of GRDF+soil application of cow dung slurry with ZnSO4 @ 20 kgha-1. Total uptake of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium by wheat crop were found to be significantly higher (138, 36 and 88 kgha-1 respectively) in treatment of application of ZnSO4 @ 20kgha-1 incubated with FYM for one week along with GRDF however, it was at par with treatment of application of ZnSO4 @ 20kgha-1 with cow dung slurry @500 Lha-1 at 30 DAS through irrigation along with GRDF. Total uptake of iron, zinc, manganese and copper were found to be significantly higher (5177, 570, 1889 and 192 gha-1 respectively) in treatment of GRDF+application of ZnSO4@ 20kgha-1 incubated with FYM for one week. Therefore, based on above findings, soil application of 100 kg FYM + ZnSO4 @20 kgha-1 incubated for one week or soil application of cow dung slurry with ZnSO4@20 kgha-1 (1:4) @500Lha-1 at 30 DAS through irrigation along with the general recommended dose of fertilizer (120:60:40 N:P2O5:K2O kg ha-1 + 10 t ha-1 FYM) to wheat was found beneficial for increase in total uptake of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, iron, zinc, manganese and copperin wheat grown on medium deep black calcareous soil.
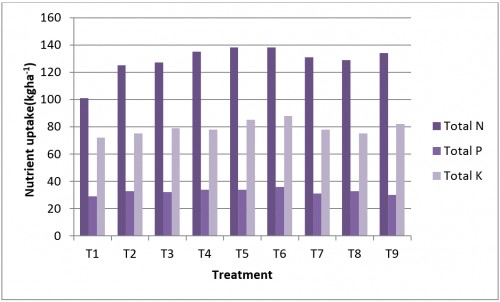
Fig. 1: Effect of methods of zinc application on total uptake of N, P and K by wheat crop at harvest stage
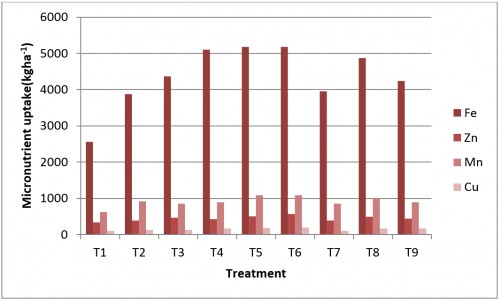
Fig. 2: Effect of different methods of zinc application on total uptake of Iron, Zinc, Manganese, copper by wheat crop at harvest stage
Pages: 1234-1239 | 455 Views 97 Downloads
download (5319KB)
How to cite this article:
Mohini Patle, AG Durgude, MR Chauhan, AD Kadlag. Effect of Zinc application on soil properties and uptake of nutrients by wheat grown on calcareous soil. Int J Chem Stud 2019;7(1):1234-1239.






