Vol. 1, Issue 4 (2013)
Adsorption of Heavy Metal (Cd2+, Cr6+ and Pb2+) from Synthetic Waste Water by Rice husk Adsorbent
Author(s): Lokendra Singh Thakur, Pradeep Semil
Abstract: Industrial waste constitutes the major source of various kinds of metal pollution in natural water. There are at least 20 metals which cannot be degraded or destroyed. The important toxic metals are Cd2+, Cr6+ and Pb2+. There are numerous methods currently employed to remove and recover the metals from our environment and many physico-chemical methods have been proposed for their removal from wastewater. Adsorption is one of the alternatives for such cases and is an effective purification and separation technique used in industry especially in water and wastewater treatments. Cost is an important parameter for comparing the adsorbent materials. Therefore, there is increasing research interest in using alternative low-cost adsorbents. The use of rice husk as the low-cost adsorbents was investigated as a replacement for current costly methods of removing heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions. The experiment results showed that maximum removal of Cadmium ion by rice husk adsorbent is 92%, Chromium ion is 83% and Lead ion are 93% at optimum condition.
Related Graphics: Click here for more related graphics
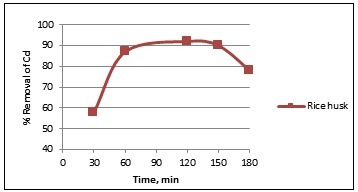
Fig. 1: Effect of contact time on cadmium (Parameter- 6 pH, Concentration 4 ppm and Dose Amount 3 gm)
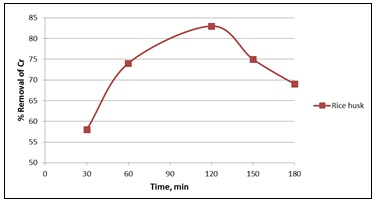
Fig. 2: Effect of contact time on chromium (Parameter- 6 pH, concentration 4 ppm and dose amount 3gm)
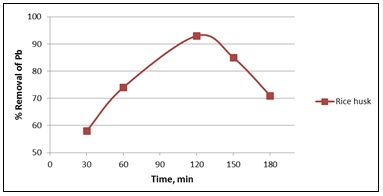
Fig. 3: Effect of contact time on lead (Parameter- 6 pH, Concentration 4 ppm and Dose Amount 3 gm)
Pages: 78-87 | 1703 Views 68 Downloads
download (6228KB)
How to cite this article:
Lokendra Singh Thakur, Pradeep Semil. Adsorption of Heavy Metal (Cd2+, Cr6+ and Pb2+) from Synthetic Waste Water by Rice husk Adsorbent. Int J Chem Stud 2013;1(4):78-87.






