Vol. 1, Issue 4 (2013)
Miscibility, Conductivity and Dielectric Studies of Poly (methyl methacrylate) and Cellulose acetate propionate Blends
Author(s): Denthaje Krishna Bhat*, H.S. Sreekantha Jois
Abstract: In the present era, material scientists are focusing on polymer blends with good miscibility and conductivity. Accordingly we report here, polymer blends of Poly (methyl methacrylate) and Cellulose acetate propionate of varying blend compositions prepared by solution casting method. The miscibility, water uptake, ion exchange capacity, proton conductivity and dielectric behavior of these blends have also been studied. The proton conductivity of the blends was found to be in the order of 10-3 S cm-1. Dimethyl formamide has been used as solvent. Fourier transform infrared spectra and differential scanning calorimetry measurements have been used to analyze the miscibility of the blends. Up to a PMMA:CAP composition of 50:50, water uptake amount of the blends showed an increasing trend. Combination of the results suggested that the variations in associated properties are due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding interaction between hydroxyl and carbonyl groups of CAP and PMMA respectively.
Related Graphics: Click here for more related graphics
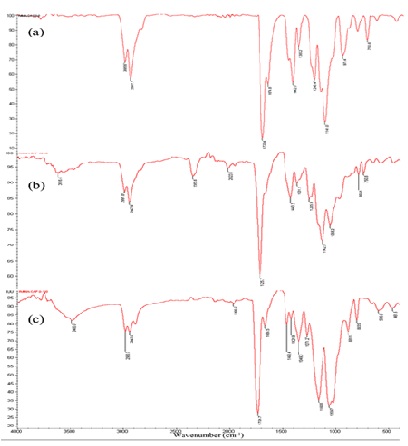
Fig. 1: (a, b, c). FTIR spectra of pure PMMA, PMMA/CAP 50/50 blend and pure CAP.
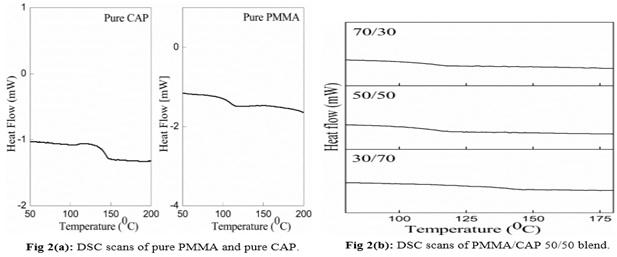
Fig. 2: images/5f.2.jpg
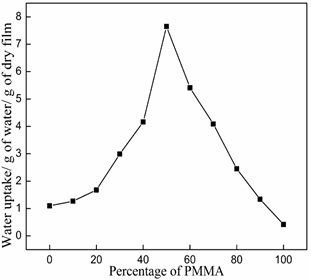
Fig. 3: Water absorption by PMMA/CAP blends.
Pages: 12-21 | 2121 Views 118 Downloads
download (5515KB)
How to cite this article:
Denthaje Krishna Bhat*, H.S. Sreekantha Jois. Miscibility, Conductivity and Dielectric Studies of Poly (methyl methacrylate) and Cellulose acetate propionate Blends. Int J Chem Stud 2013;1(4):12-21.






