Vol. 1, Issue 2 (2013)
Influence of Some Phosphates on The Rate of Calcium Sulfate Dihydrate Crystalistion in sodium Chloride Solution
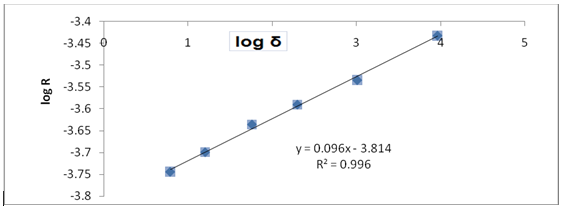
Fig. 1: Plots of Log R against Log δ
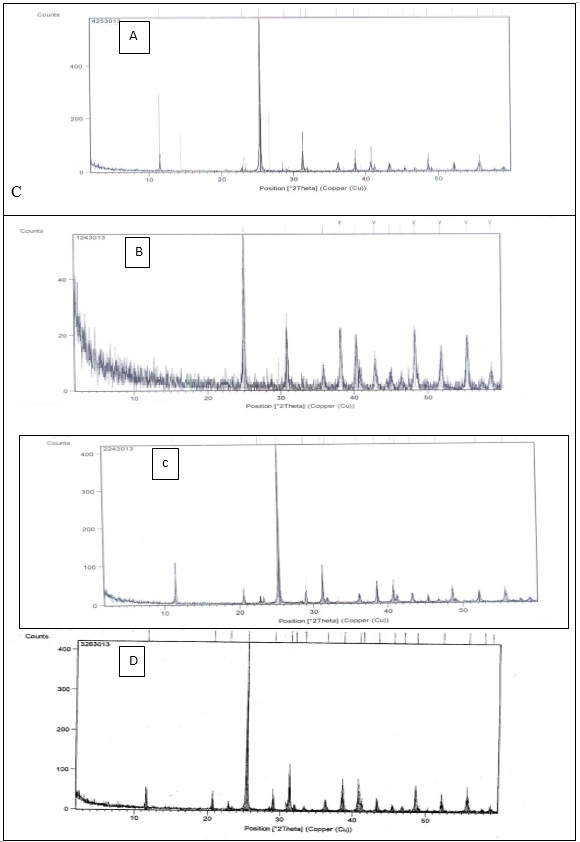
Fig. 2: XRD analysis of calcium sulfate dihydrate (A) in absence of all additives (B),(c) ,(d) in the presence of 10-7 M of additives 1,2,3 respectively
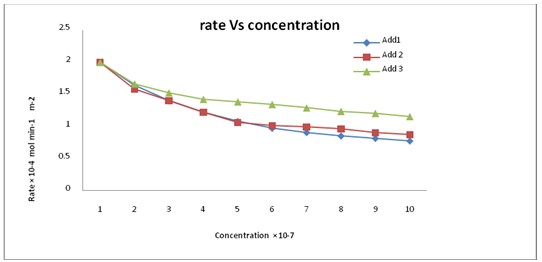
Fig. 3: Effect of Add1 and Add2 and Add3 on rates of crystallization of calcium sulfate dihydrate crystals at δ = 1.32, I = 0.15 mol dm-3, PH=3and 50 mg seed
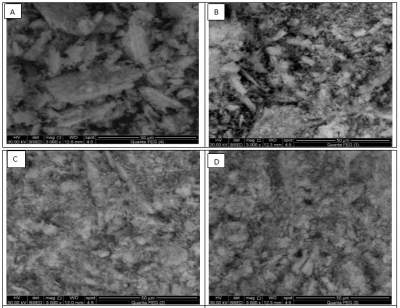
Fig. 4: Scanning electron micrographs of calcium sulfate dihydrate (A) in absence of Additives and (b,c,d) in the presence of 10-7 M additives 1,2,3 respectively

Fig. 5: Effect of supersaturation degree (δ) on the rate of crystallization of calcium sulfate dihydrate crystals at pH=3, T= 25 ºc, I = 0.15 mol dm -3, and 50 mg seed in absence of inhibitors and in presence of additives
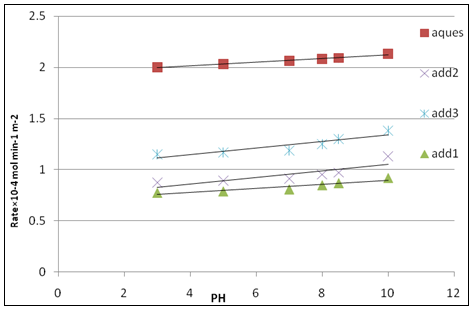
Fig. 6: Effect of pH on the rate of crystallization of calcium sulfate dihydrate crystals at δ = 1.32, T = 25 ºc, I = 0.15 mol dm -3, and 50 mg seed in absence of inhibitors and in presence of inhibitors
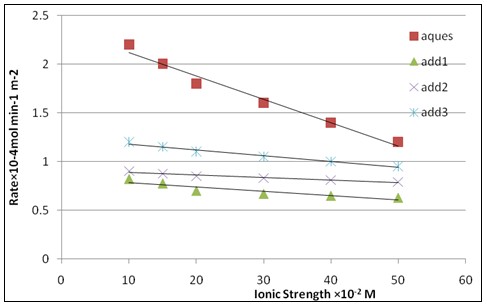
Fig. 7: Effect of ionic strength (I) on the rate of crystallization of calcium sulfate dihydrate crystals at δ = 1.32, pH=3, T = 25 ºc and 50 mg seed in absence of inhibitors and in presence of phosphate inhibitors
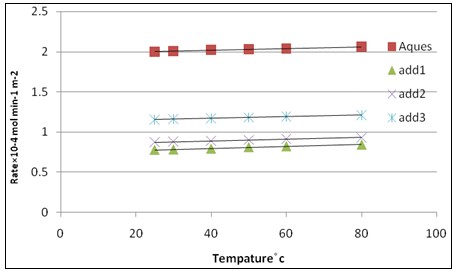
Fig. 8: Effect of temperature on the rate of crystallization of calcium sulfate dihydrate crystals at δ = 1.32, pH=3, I = 0.15 mol dm-3 and 50 mg seed in absence of inhibitors and in presence of inhibitors




