Vol. 1, Issue 2 (2013)
Influence of Some Phosphates on The Rate of Calcium Sulfate Dihydrate Crystalistion in sodium Chloride Solution
Author(s): N. S. Yehia, W. K. Saif elyazal, A. M. Heneash, I. A. Ibrahem
Abstract: Crystallization of calcium sulfate dihydrate (CaSO4.2H2O) in sodium chloride solutions at different supersaturation (δ = 1.2–2.49), pH =3, ionic strength (I = 0.15 M) and at 25°C was studied. The influence of disodium hydrogen phosphate and sodium tripolyphosphate and disodium dihydrogen phosphate having very low concentrations (10-7 mol dm-1) on the rate of crystallization at different supersaturation was investigated. The rate of crystallization was found to be dependent of the stirring rate suggesting diffusion mechanism. The addition of all additives retarded the rate of crystallization to an extent proportional to their amounts present. Furthermore, the retardation effect was enhanced as the supersaturation decreases. The results also revealed that the increase in both pH (3 −10) and crystallization temperature (20 −80 oC) brought about an increase in calcium sulfate crystallization rate.
Related Graphics: Click here for more related graphics
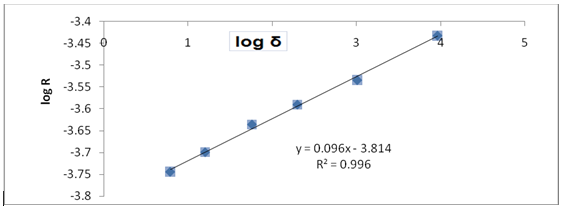
Fig. 1: Plots of Log R against Log δ
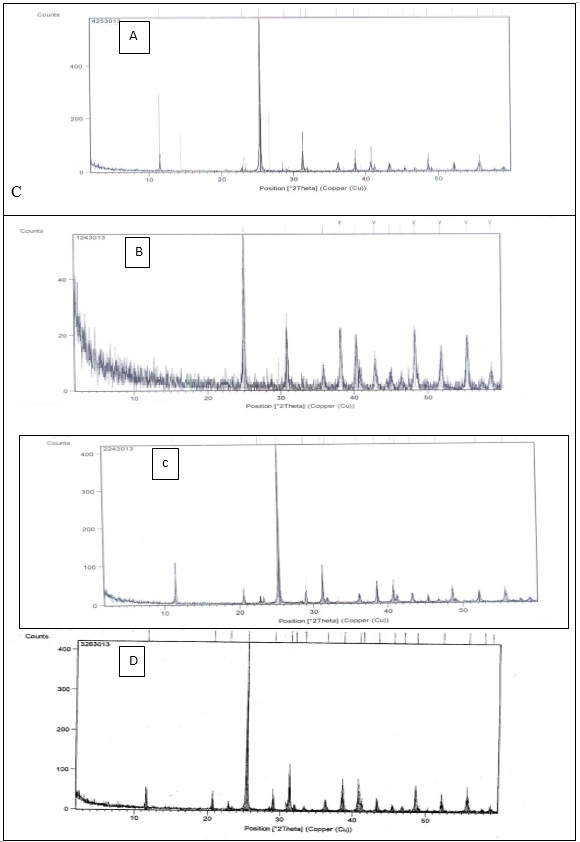
Fig. 2: XRD analysis of calcium sulfate dihydrate (A) in absence of all additives (B),(c) ,(d) in the presence of 10-7 M of additives 1,2,3 respectively
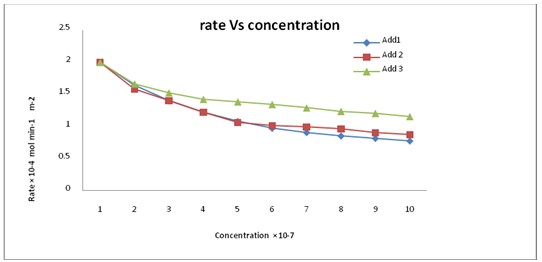
Fig. 3: Effect of Add1 and Add2 and Add3 on rates of crystallization of calcium sulfate dihydrate crystals at δ = 1.32, I = 0.15 mol dm-3, PH=3and 50 mg seed
Pages: 68-78 | 1965 Views 101 Downloads
download (39264KB)
How to cite this article:
N. S. Yehia, W. K. Saif elyazal, A. M. Heneash, I. A. Ibrahem. Influence of Some Phosphates on The Rate of Calcium Sulfate Dihydrate Crystalistion in sodium Chloride Solution. Int J Chem Stud 2013;1(2):68-78.






